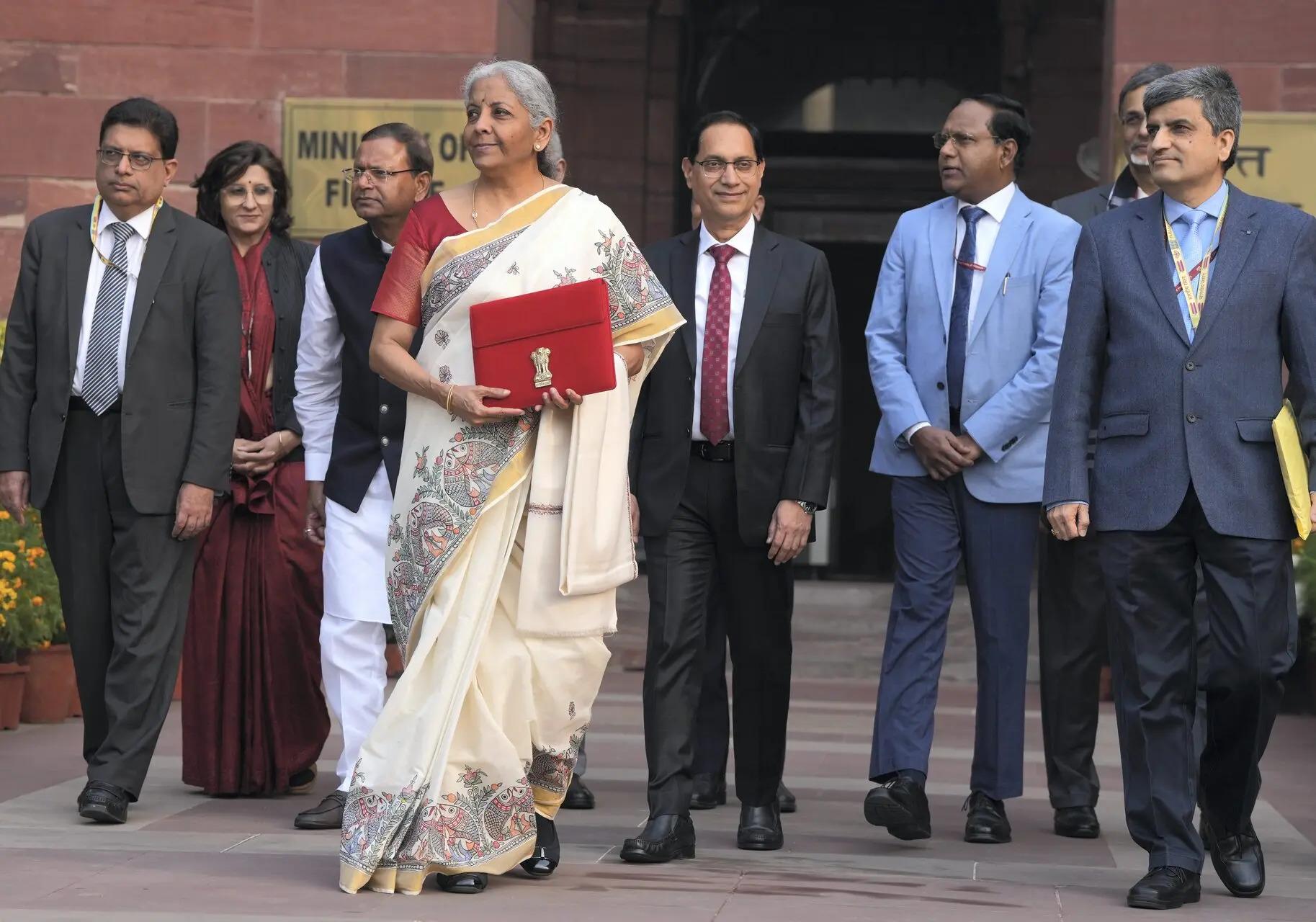
Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has arrived at Parliament for her eighth consecutive Union Budget presentation today, February 1, 2025. Earlier, she met with President Droupadi Murmu to seek approval for the Budget. The Union Cabinet is now set to meet before the Budget speech at 11 am.
This year’s Budget is highly anticipated, with expectations for increased capital expenditure (capex) and income tax relief for salaried individuals. On January 31, the first part of the Budget Session began with the release of the Economic Survey 2025 by FM Sitharaman.
India Inc. is looking forward to the government’s measures to boost infrastructure, improve the ease of doing business, and allocate resources for the development of artificial intelligence (AI), among other initiatives.
Sitharaman’s Budget speech today will mark her eighth consecutive presentation and her second full Budget under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s leadership in his third term, Modi 3.0.
Follow live updates on the Budget presentation below.
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman stands to present the Budget for 2025-2026.
Budget 2025-26 Focuses on Reforms, Agri Growth
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman began her speech by saying, “We aim to unlock India’s potential under Prime Minister Modi’s leadership. The Union Budget for 2025-26 is focused on accelerating growth.” She highlighted that this budget is dedicated to growth, with a vision for a “Viksit Bharat.” India’s economy is currently the fastest growing among major economies.

The Budget 2025-26 continues the government’s efforts to boost growth and ensure inclusive development. It aims to uplift household sentiment and empower the middle class.
The budget focuses on key areas like farmers, youth, and women (GYAN). It also aims to secure energy supplies and promote exports, with agriculture, MSMEs, and exports seen as key growth engines.
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman says the Budget focuses on transformative reforms in six key areas: taxation, the financial sector, power, urban development, mining, and regulatory reforms. These sectors are crucial for driving growth, improving infrastructure, and ensuring sustainable development.
A major announcement for agriculture will benefit 1.7 crore farmers. Under the Prime Minister Krishi Yojana, the government will launch a new agricultural district program, partnering with states. This will target 100 districts with low productivity and improve farming through crop diversification, better irrigation, increased credit access, and improved post-harvest storage.
India Launches 6-Year Mission for Pulse Self-Reliance
Finance Minister announced a 6-year mission to make India self-reliant in pulses, focusing on tur and masoor. Agencies like NAFED and NCCF will help procure these pulses from registered farmers. The plan includes setting up a Makhana Board in Bihar and launching a national mission for high-yielding seeds. This initiative aims to support farmers and ensure guaranteed procurement.
Budget 2025-26 Focuses on Agriculture, Nutrition, Cotton
The Finance Minister outlined plans for a healthier India, focusing on promoting the consumption of vegetables, fruits, and nutritious foods. This shift, driven by rising income levels, aims to improve nutrition for a broader population. The government will introduce initiatives to increase the availability and accessibility of these essential food items.
In agriculture, the Finance Minister announced an increase in the loan limit under the Kisan Credit Cards (KCC) scheme, raising it from ₹3,000 to ₹5,000 to support 7.7 crore farmers, fishermen, and dairy farmers. The budget also introduced the Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana, focusing on 100 low-productivity districts to boost agriculture. A national mission to ensure self-reliance in edible oils and seeds, and a six-year mission for pulses self-sufficiency, were also announced. Additionally, the government will create a Makhana Board in Bihar for better processing and value addition.
For cotton, a new mission to improve cotton productivity, focusing on Extra Long Staple Cotton, aims to enhance quality and rejuvenate India’s traditional textile sector.
FM Focuses on MSMEs, Women Entrepreneurs, and Manufacturing
Finance Minister highlighted MSMEs as the second engine of growth, contributing 45% to India’s exports. To support their growth, the government has increased the classification limit for MSMEs and introduced customized credit cards for micro-enterprises. A new scheme will provide term loans to 5 lakh women entrepreneurs and first-time business owners over the next five years. The Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups has been increased to ₹20 crore. The FM also announced plans for India to become a global hub for toys. Additionally, an institute will be set up in Bihar for food processing, and the National Manufacturing Mission will further boost the “Make in India” initiative.
FM Announces Key Initiatives for Growth, Education, and Health
Finance Minister revealed several initiatives aimed at boosting growth and development. A National Manufacturing Mission will provide policy support to industries, with a focus on clean tech and domestic production of EV batteries and solar panels. Investments are considered the third engine of growth. The government will also support 8 crore children through the Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 programs. In education, Atal Tinkering Labs will be set up in government schools over the next five years, while the Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme will promote mother tongue languages. To enhance skills, five National Centres of Excellence for skilling will be created, and additional infrastructure will be added to five IITs. On health, cancer centers will be established in all district hospitals, and three Centres of Excellence on AI for education will be set up with ₹500 crore in funding.
FM Announces Jal Jeevan, Nuclear Energy, and Infra Plans
Finance Minister announced that the Jal Jeevan Mission will be extended until 2028, aiming for 100% coverage, with 80% of rural areas already having access since 2019. She also highlighted a nuclear energy mission to achieve 100 GW, supporting the vision of a “Viksit Bharat.”
For infrastructure, state capex-linked loans are set at ₹1.5 lakh crore for FY26, and a ₹1 lakh crore Urban Challenge Fund will be created to redevelop cities. The government will launch a 2025-30 asset monetization plan and each infrastructure ministry will submit a three-year list of PPP projects.
Additionally, ministries will propose three PPP projects each, with ₹1.5 lakh crore in interest-free loans for capex and incentives for reforms.
The development of 100 GW of nuclear energy by 2047 under the Nuclear Energy Mission for a Viksit Bharat will involve amendments to the Atomic Energy Act.
FM Announces New Tax Code, Export Boost Plans
FM announced a new Income Tax code will be introduced next week, aiming to build trust by scrutinizing taxes later. The Insurance FDI limit will be increased from 74% to 100%. The government has previously implemented faceless assessments, faster tax returns, and Vivad Se Vishwas schemes. Exports are the 4th engine of growth, with a new Export Promotion Mission and digital infrastructure for international trade. Support will also be provided to domestic manufacturers to join global supply chains and promote GCCs in tier-two cities.
FM says government is committed to facilitating business by ensuring quicker approvals for company mergers and expanding the scope of these regulations. It aims to establish a modern, people-friendly, trust-based regulatory framework to promote ease of doing business.
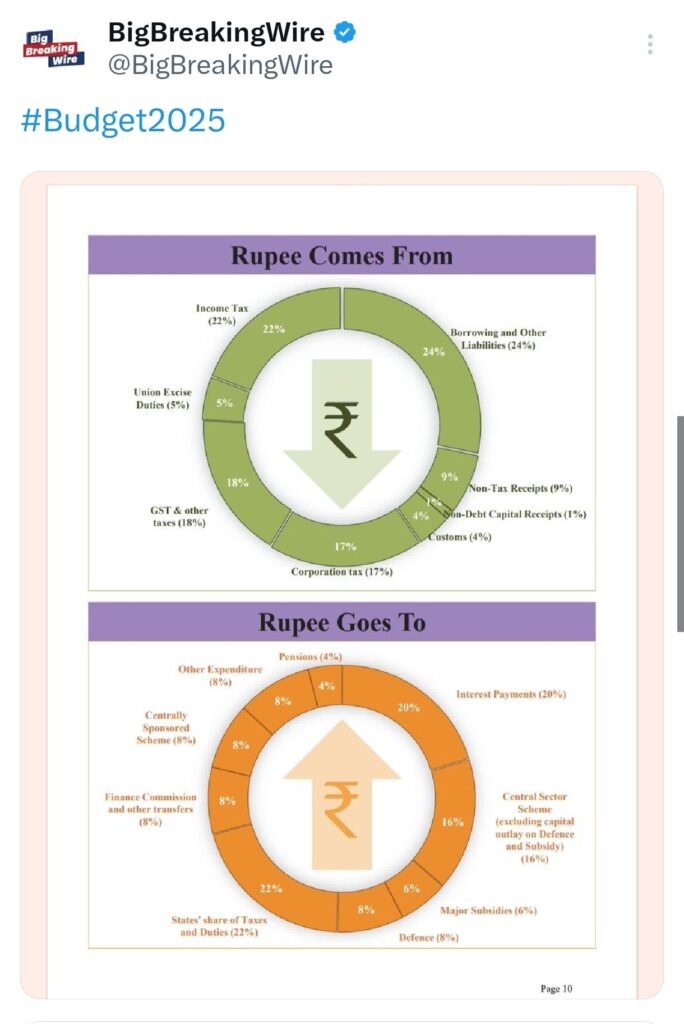
India’s Fiscal Path: 2024-25 Budget Highlights and Deficit Projections
Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman mentioned that the government plans to keep the fiscal deficit in check each year, ensuring that central government debt decreases as a percentage of GDP. The fiscal roadmap for the next six years is outlined in the FRBM statement. For 2024-25, the total receipts (excluding borrowings) are estimated at ₹31.47 lakh crore, with net tax receipts at ₹25.57 lakh crore. The total expenditure is expected to be ₹47.16 lakh crore, which includes ₹10.1 lakh crore for capital expenditure. The fiscal deficit for the year is projected to be 4.8% of GDP.
India’s Customs Tariff Rationalisation in Budget 2025
The government plans to simplify the customs tariff structure to reduce duty inversion and support domestic manufacturing, value addition, and exports. This change is part of a wider review started in the July 2024 Budget.
As part of the 2025 Budget, seven more tariff rates will be removed, following the removal of seven rates in the 2023-24 Budget. This will leave just eight tariff rates, including a zero rate. Most duty rates will stay the same, with only a few items seeing a slight reduction.
The government will exempt Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on cobalt powder, lithium-ion battery scrap, lead, zinc, and 12 other essential minerals to encourage domestic manufacturing and value addition.
35 more items for electric vehicle (EV) battery production and 28 more items for mobile phone battery production will be added to the list of exempted capital goods.
Personal Income Tax (PIT) reforms, along with simplifying Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) and Tax Collected at Source (TCS), will reduce the compliance burden.
TDS threshold for senior citizens is increased from Rs 50,000 to Rs 1 lakh.
TCS on Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS) is increased to Rs 10 lakh from Rs 7 lakh. TCS on remittances for education, using loans from specified financial institutions, has been removed. The TDS threshold limit for rent is raised to Rs 6 lakh.

No income tax payable upto 12 lakh.
Big relief for the middle class! The new tax slabs under the revised regime are as follows:
Rs 4 to 8 lakh: 5%
Rs 8 to 12 lakh: 10%
Rs 12 to 16 lakh: 15%
Rs 16 to 20 lakh: 20%
Rs 20 to 24 lakh: 25%
Above Rs 24 lakh: 30%
A person earning Rs 18 lakh annually will benefit by Rs 70,000 in taxes, while those with an annual income of Rs 12 lakh will see a tax relief of Rs 80,000.
The government plans to forgo Rs 1 lakh crore in direct taxes and Rs 2,600 crore in indirect taxes due to changes in tax rates.
Tax Changes: The government has reduced tax liability under the Income Tax. The nil tax slab has been raised from Rs 7 lakh to Rs 12 lakh under the old regime. In the new tax regime, the tax slabs and liabilities have been lowered, offering benefits ranging from Rs 70,000 to Rs 1.1 lakh for income earners in the Rs 12 lakh to Rs 25 lakh range.

Bringing you the latest updates on finance, economies, stocks, bonds, and more. Stay informed with timely insights.









2 Comments