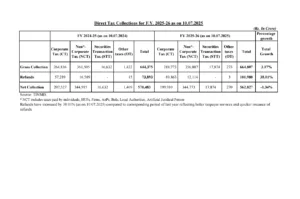
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is expected to lower benchmark interest rates by 50-75 basis points (bps) in the 2025-26 financial year, according to CRISIL’s India Outlook 2025 report. The move aims to reduce borrowing costs and support consumer spending.
Expected Impact of Rate Cuts
A reduction in interest rates generally helps in boosting consumption, as it gradually leads to lower lending rates across the economy. This makes borrowing more affordable for businesses and individuals, encouraging spending and investment.
Past Rate Decisions
The RBI had kept the repo rate steady at 6.50% for 11 consecutive policy meetings before finally cutting it by 25 bps in February 2025. This was the first rate cut in nearly five years, introduced to stimulate a slowing economy. Previously, the central bank had raised the repo rate by 250 bps between May 2022 and February 2023 to control inflation. Since April 2023, the rate had remained unchanged at 6.5% to maintain price stability.
India’s Growth Outlook
CRISIL projects India’s economy to grow at 6.5% in 2025-26, maintaining its position as one of the fastest-growing major economies. This growth will be supported by an easing monetary policy, government efforts to boost private consumption, and a 10.1% rise in capital expenditure (capex) as announced in the Union Budget.
However, the government is also working to reduce the fiscal deficit from 4.8% of GDP in FY25 to 4.4% in FY26. While this will lower the fiscal stimulus, the overall economic expansion is expected to remain stable.
Risks from Global Factors
Despite a positive domestic outlook, emerging global risks could impact India’s exports and add uncertainty to private sector investments. Factors such as geopolitical tensions and volatility in global trade will be key areas to watch.
Recent Economic Trends
India’s economy rebounded in the December 2024 quarter, growing at 6.2% after hitting a seven-quarter low of 5.6% in July-September. The agriculture and services sectors played a key role in this recovery.
On the expenditure side, both private and government consumption saw improvement. However, capital formation, which indicates investment activity, grew only 5.7% compared to 5.8% in the previous quarter. Over the full fiscal year, fixed capital formation slowed to 6% from 9.8%, while private consumption rose from 5.3% in FY24 to 6.8% in FY25.
Inflation and Commodity Prices
Inflation is expected to ease further in FY26, helped by good rabi crop sowing, which was up 1.5% year-on-year as of February 4. This should improve food supply and keep prices stable.
Additionally, lower crude oil and commodity prices will help keep core inflation within RBI’s comfort range. CRISIL Intelligence estimates crude oil prices to average between $70-75 per barrel in FY26, down from $78-83 per barrel in FY25.
Conclusion
With stable inflation, moderate interest rate cuts, and strong domestic demand, India’s economy is set to maintain steady growth in the next financial year. However, global uncertainties and investment trends will play a crucial role in shaping the overall outlook.
Bringing you the latest updates on finance, economies, stocks, bonds, and more. Stay informed with timely insights.












[…] India Set to Become the World’s Third-Largest Economy by 2028: Morgan StanleyRBI Likely to Cut Interest Rates by 50-75 bps in 2025-26 to Boost Economy: CRISIL Reportbigbreakingwire […]