India’s industrial production grew by only 1.2% in May 2025, down from 2.6% in April, according to data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. This is the slowest growth rate in eight months and signals a broader industrial slowdown.
Industrial Production Overview
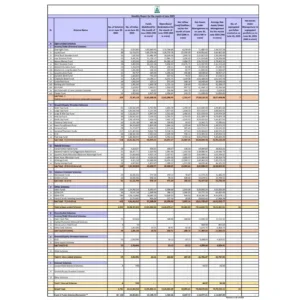
The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) stood at 156.6 in May 2025, slightly higher than 154.7 in May 2024. However, the pace of expansion remained weak:
Actual growth: 1.2%
Expected: 2.4%
Previous (April): 2.7%
Cumulative IIP growth for April–May 2025 held steady at 1.8%, sharply lower than 4.1% in the same period last year.
Sector-Wise Highlights
Manufacturing output rose 2.6%, lower than April’s 3.4%
Mining sector contracted 0.1%
Electricity generation fell 5.8%, the steepest drop in five years due to excess rainfall
Use-Based Industry Performance
Capital goods: +14.1%
Infrastructure and construction goods: +6.3%
Consumer durables: -0.7%
Consumer non-durables: -2.4%
Primary goods: -1.9%
In the manufacturing segment, 13 out of 23 industry groups recorded positive growth. Notable contributions came from:
Machinery and equipment: +11.8%
Basic metals: +6.4%
Non-metallic mineral products: +6.9%
Key items driving growth included cement, glass, pumps, and steel products.
Fiscal Deficit Falls to 0.8% of Annual Target
India’s fiscal deficit for April–May 2025 was Rs 13,163 crore, just 0.8% of the full-year FY26 target of Rs 15.68 lakh crore. In the same period last year, the deficit stood at 3.1% of the FY25 target.
This improvement was largely due to the Rs 2.69 lakh crore dividend transferred by the Reserve Bank of India in May — the highest ever.
Revenue surplus: Rs 1.83 lakh crore (34.9% of FY26 target)
Total expenditure: Rs 7.46 lakh crore (14.7%)
Revenue expenditure: Rs 5.25 lakh crore (13.3%)
Capital expenditure: Rs 2.21 lakh crore
Key spending components within revenue:
Interest payments: Rs 1.47 lakh crore
Major subsidies: Rs 51,253 crore
Strong Revenue Collection
Total receipts (April–May): Rs 7.33 lakh crore (21% of FY26 target)
Net tax revenue: Rs 3.5 lakh crore (12.4%)
Non-tax revenue: Rs 3.57 lakh crore (61.2%)
Non-debt capital receipts stood at Rs 25,224 crore, which is 33.2% of the full-year target, a sharp rise from 2.7% during the same period last year.
The Centre also transferred Rs 1.63 lakh crore to states as their share in central taxes — Rs 23,720 crore more than last year.
Summary
India’s industrial output lost momentum in May, with electricity and consumer sectors dragging overall growth. However, strong fiscal performance, driven by the RBI’s record dividend, has kept the government’s finances in a solid position early in the fiscal year.

BBW News Desk is the editorial team of BigBreakingWire, a digital newsroom focused on global finance, markets, geopolitics, trade policy, and macroeconomic developments.
Our editors monitor government decisions, central bank actions, international trade movements, corporate activity, and economic indicators to deliver fast, fact-based reporting for investors, professionals, and informed readers.
The BBW News Desk operates under the editorial standards of BigBreakingWire, prioritizing accuracy, verified information, and timely updates on major global developments.







































Be First to Comment