India’s economic outlook remains strong. As presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in Parliament, the macroeconomic framework shows solid growth, controlled deficit, and high capital investment.
What is India’s GDP Growth for FY 2025-26?
- Real GDP growth estimated at 7.4%
- Nominal GDP growth estimated at 8%
- Services sector growth: 9.1% (main growth driver)
- Manufacturing and construction growth: 7%
- Agriculture growth: 3.1%
What is the GDP Projection for FY 2026-27?
Nominal GDP is projected to grow by 10% over FY 2025-26 First Advance Estimates.
Consumption and Demand Trends
- Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE) growth: 7%
- PFCE share in GDP: 61.5% (highest since FY12)
- Government consumption growth: 5.2% in FY26
- Strong demand seen in UPI, air traffic, rail travel, and e-way bills
Investment Growth
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) growth: 7.8%
- GFCF share in GDP: ~30% for last 3 years
External Sector Performance
- Total exports FY25: USD 825.3 billion
- Merchandise export growth (Apr-Dec 2025): 2.4%
- Services export growth: 6.5%
- FDI inflows FY25: USD 81 billion
- Current Account Deficit reduced to 0.8% of GDP in H1 FY26 (from 1.3%)
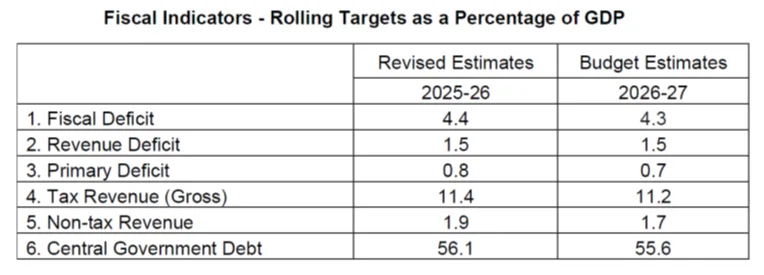
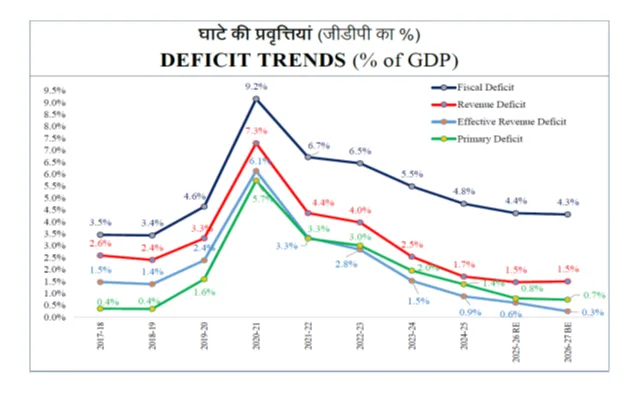
Fiscal Deficit and Debt Position
- Fiscal Deficit FY 2025-26 RE: 4.4%
- Fiscal Deficit FY 2026-27 BE: 4.3%
- Central Government Debt to GDP FY 2026-27: 55.6%
- Medium-term debt target: 50±1% by FY31
Revenue Deficit
- Revenue Deficit FY 2026-27: 1.5%
- Effective Revenue Deficit: 0.3%
Government Receipts
- Gross Tax Revenue: Rs 44.04 lakh crore
- Direct Taxes: Rs 26.97 lakh crore
- Indirect Taxes: Rs 17.07 lakh crore
- Tax to GDP ratio: 11.2%
- Non-Tax Revenue: Rs 6.66 lakh crore
- Total Revenue Receipts: Rs 35.33 lakh crore
Government Expenditure
- Total expenditure: Rs 53.47 lakh crore
- Capital expenditure: Rs 12.22 lakh crore
- Grants for asset creation: Rs 4.93 lakh crore
- Effective Capital Expenditure: Rs 17.15 lakh crore (4.4% of GDP)
Money Shared with States
- Tax Devolution to States: Rs 15.26 lakh crore
- Finance Commission Grants: Rs 1.4 lakh crore
- Total Resources to States: Rs 16.56 lakh crore
- States’ share in divisible tax pool: 41%
India Sticks to Fiscal Discipline as Deficit Falls and Capex Stays Strong
Nirmala Sitharaman said India’s debt to GDP ratio is projected at 55.6% in BE 2026-27 versus 56.1% in RE 2025-26, with a glide path toward about 50±1% by 2030-31. Fiscal deficit is 4.4% of GDP in RE 2025-26 and estimated at 4.3% of GDP in BE 2026-27.
RE 2025-26 non debt receipts are Rs 34 lakh crore, including Rs 26.7 lakh crore net tax receipts. Total expenditure is Rs 49.6 lakh crore, with capital expenditure at Rs 11 lakh crore.
BE 2026-27 non debt receipts are estimated at Rs 36.5 lakh crore, total expenditure at Rs 53.5 lakh crore, and net tax receipts at Rs 28.7 lakh crore. Net market borrowing is estimated at Rs 11.7 lakh crore and gross market borrowing at Rs 17.2 lakh crore.
Why is This Important?
India’s economy is supported by strong domestic demand, rising investments, stable inflation, improving exports, and fiscal discipline. High capital spending is expected to drive future growth and job creation.
Quick Summary
- India GDP growth strong at 7.4%
- Fiscal deficit controlled at 4.3%
- Capital spending very high at Rs 17.15 lakh crore
- Debt ratio declining
- Exports and FDI remain strong
Fitch Ratings flags slower deficit control in India, says Budget impact on growth neutral
Slower Deficit Reduction, Growth Impact Seen NeutralFitch Ratings says India’s latest federal budget shows the government is reducing the deficit at a slower pace now. According to the agency, cutting the deficit further is becoming more difficult without putting pressure on economic growth.
It added that the overall budget is broadly neutral for growth. This means the budget is not expected to strongly boost or hurt the economy but instead maintain balance during a period of global uncertainty.
The government has set a fiscal deficit target of 4.3% of GDP and aims for a debt to GDP level of 55.6% in 2026–27, while continuing to support manufacturing and economic stability.
S&P Supports India Fiscal Plan, Flags Tariff Risk, Sees US Deal Boost
S&P Global Ratings says India’s latest Budget supports its view that the government is following a path of gradual fiscal consolidation. The agency believes policy steps in the Budget match its expectations for disciplined fiscal management and stronger macro stability.
At the same time, S&P notes that the recent spike in effective US tariffs is putting pressure on India’s export oriented manufacturing growth. Higher trade barriers are making it harder for some sectors to expand through overseas demand.
However, the agency adds that a trade agreement with the United States could reduce uncertainty and lift business confidence. This would especially help labor intensive sectors, giving broader support to jobs and industrial growth in India.

BBW News Desk is the editorial team of BigBreakingWire, a digital newsroom focused on global finance, markets, geopolitics, trade policy, and macroeconomic developments.
Our editors monitor government decisions, central bank actions, international trade movements, corporate activity, and economic indicators to deliver fast, fact-based reporting for investors, professionals, and informed readers.
The BBW News Desk operates under the editorial standards of BigBreakingWire, prioritizing accuracy, verified information, and timely updates on major global developments.
























Be First to Comment