Technical analysis is a popular method used by traders and investors to evaluate and predict future price movements in the stock market, cryptocurrencies, forex, and other financial instruments. Unlike fundamental analysis, which looks at a company’s financial health, technical analysis focuses on price action, volume, and historical patterns.
In this article, you’ll learn everything you need to know about technical analysis — from its basic principles to the tools and strategies used by professional traders.
Note: This is just an intro. More deep analysis & strategies coming soon. Stay connected!
Table of Contents
1. What is Technical Analysis?
2. Key Principles of Technical Analysis
3. Types of Technical Charts
4. Common Technical Indicators
5. Support and Resistance
6. Candlestick Patterns
7. Chart Patterns Every Trader Should Know
8. Timeframes in Technical Analysis
9. Limitations of Technical Analysis
10. Final Thoughts
What is Technical Analysis?
Technical analysis is a method of forecasting price direction by analyzing past market data, primarily price and volume. It is based on the idea that “history tends to repeat itself” in predictable patterns and that all known information is already reflected in the price.
Traders use technical analysis to identify entry and exit points, plan risk management, and make informed decisions — whether for short-term trades or long-term investments.
Key Principles of Technical Analysis
1. Market Discounts Everything
This principle suggests that all factors — company fundamentals, news, economic data — are already reflected in the asset’s price. So, analysts focus on price action only.
2. Price Moves in Trends
Prices move in trends: uptrends, downtrends, or sideways (range-bound). Identifying these trends helps traders follow the market rather than fight it.
3. History Repeats Itself
Human psychology and market behavior tend to repeat over time. Technical analysis leverages this idea using patterns and indicators to forecast future movement.
Types of Technical Charts
1. Line Chart
Simple and clean
Plots closing prices over time
Good for beginners
2. Bar Chart
Shows open, high, low, and close (OHLC)
Gives more details than a line chart
3. Candlestick Chart
Most popular
Displays OHLC data using visual candles
Great for spotting patterns and trends
Common Technical Indicators
Technical indicators help traders measure trends, momentum, volatility, and volume. Here are some popular ones:
1. Moving Averages (MA)
Smoothens price data
Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
Used to identify trend direction
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Measures momentum
Scale: 0 to 100
Above 70 = Overbought, Below 30 = Oversold
3. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Tracks trend strength and reversals
Consists of MACD line, signal line, and histogram
4. Bollinger Bands
Measures volatility
Composed of a middle moving average and two outer bands
Prices tend to return to the mean
5. Volume
Indicates the strength of a price move
High volume = strong move, Low volume = weak move
Support and Resistance
What is Support?
Support is a price level where buying interest is strong enough to prevent further decline. Traders often place buy orders near support levels.
What is Resistance?
Resistance is a price level where selling interest is strong enough to stop price from rising. Traders often take profits or short here.
Why Are They Important?
Helps identify entry/exit points
Used to place stop-loss or target levels
Often aligns with key psychological levels
Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns are visual indicators of market sentiment. Some common types include:
1. Doji

Indicates indecision
Often appears before reversals
2. Hammer

Bullish reversal pattern
Appears after a downtrend
3. Shooting Star
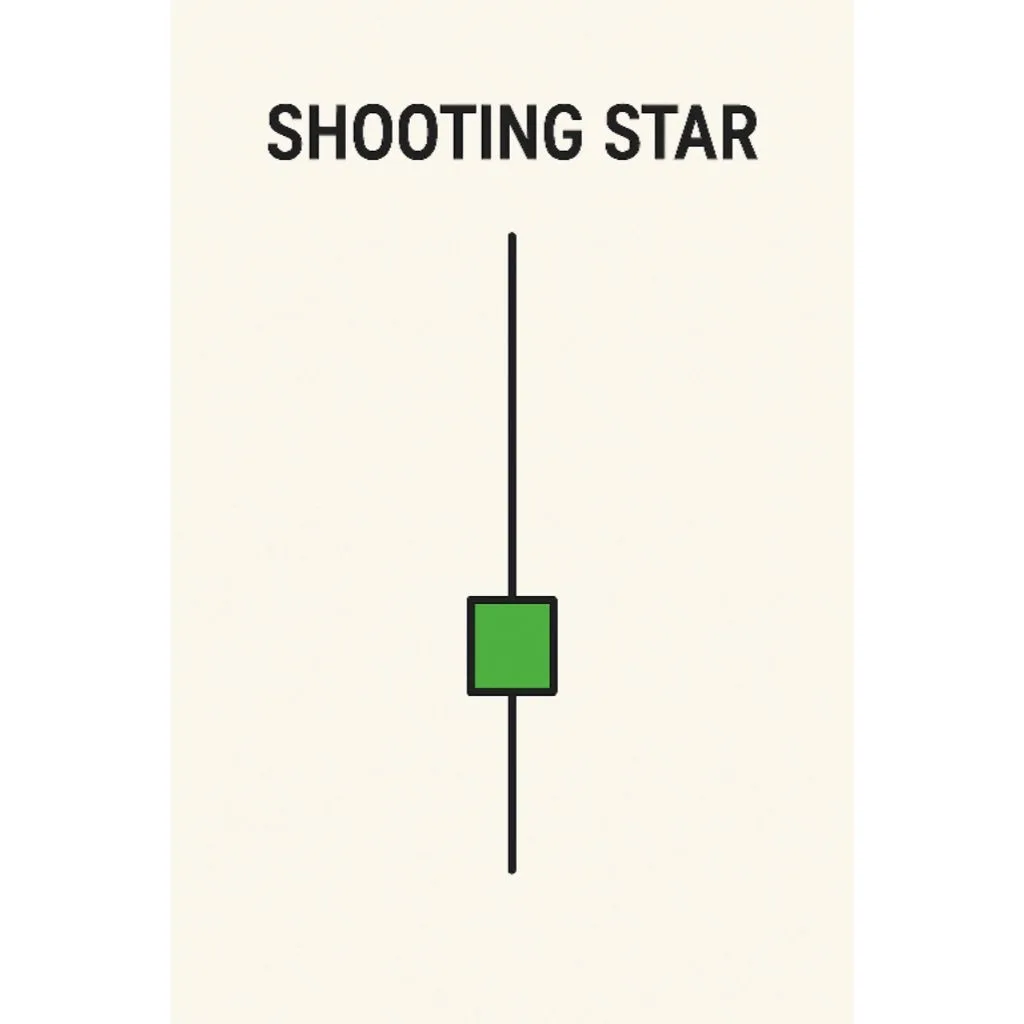
Bearish reversal pattern
Appears after an uptrend
4. Engulfing Patterns
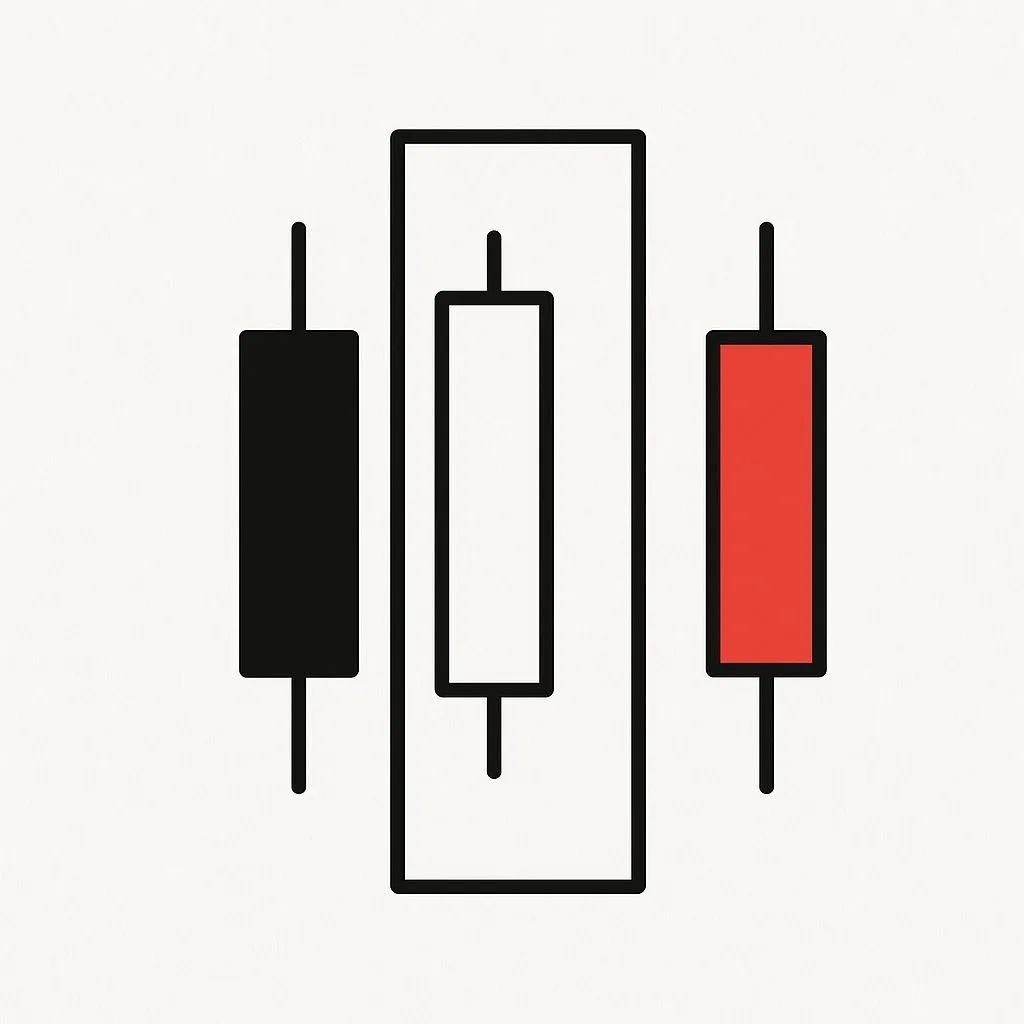
Bullish or bearish
Shows strong reversal when a candle fully engulfs the previous one
Chart Patterns Every Trader Should Know
Chart patterns help predict future price moves. These patterns are categorized into continuation and reversal patterns.
1. Head and Shoulders
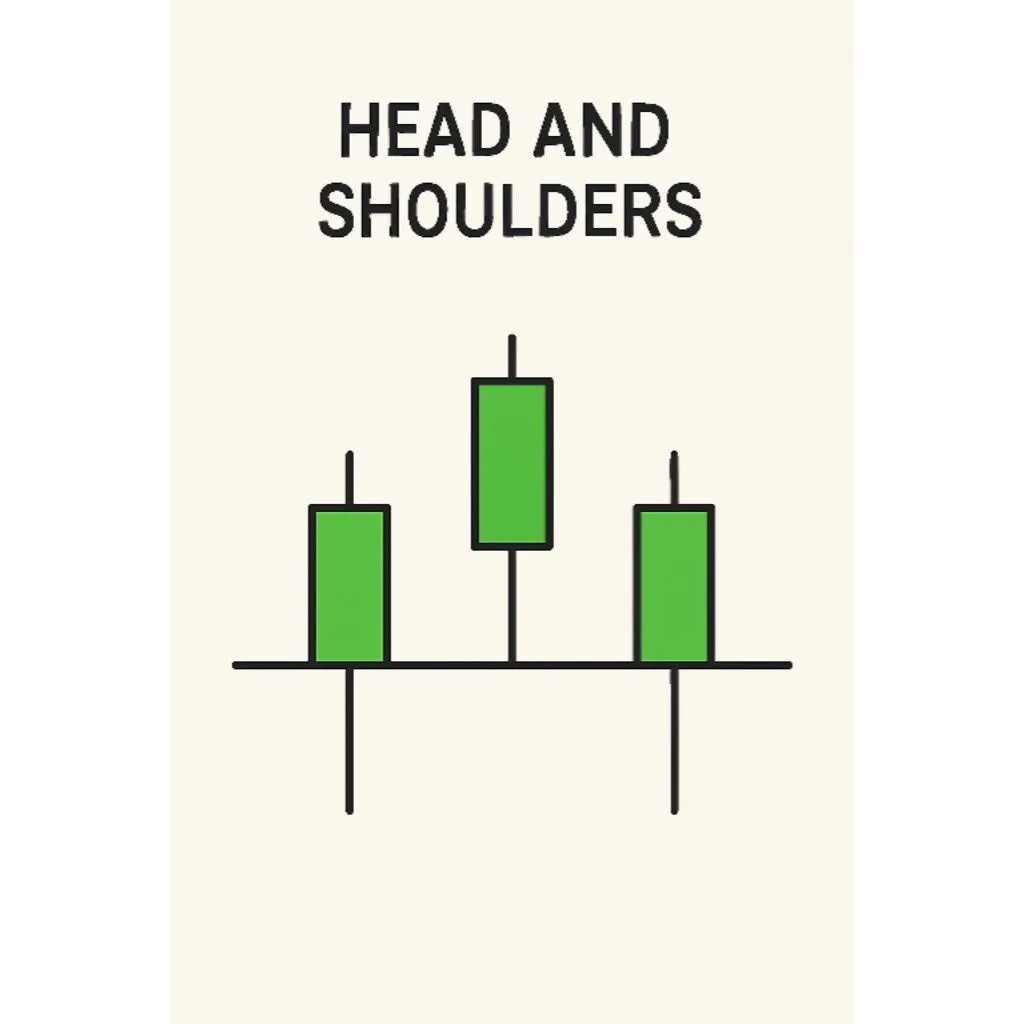
Reversal pattern
Signals trend change (top or bottom)
2. Double Top and Double Bottom
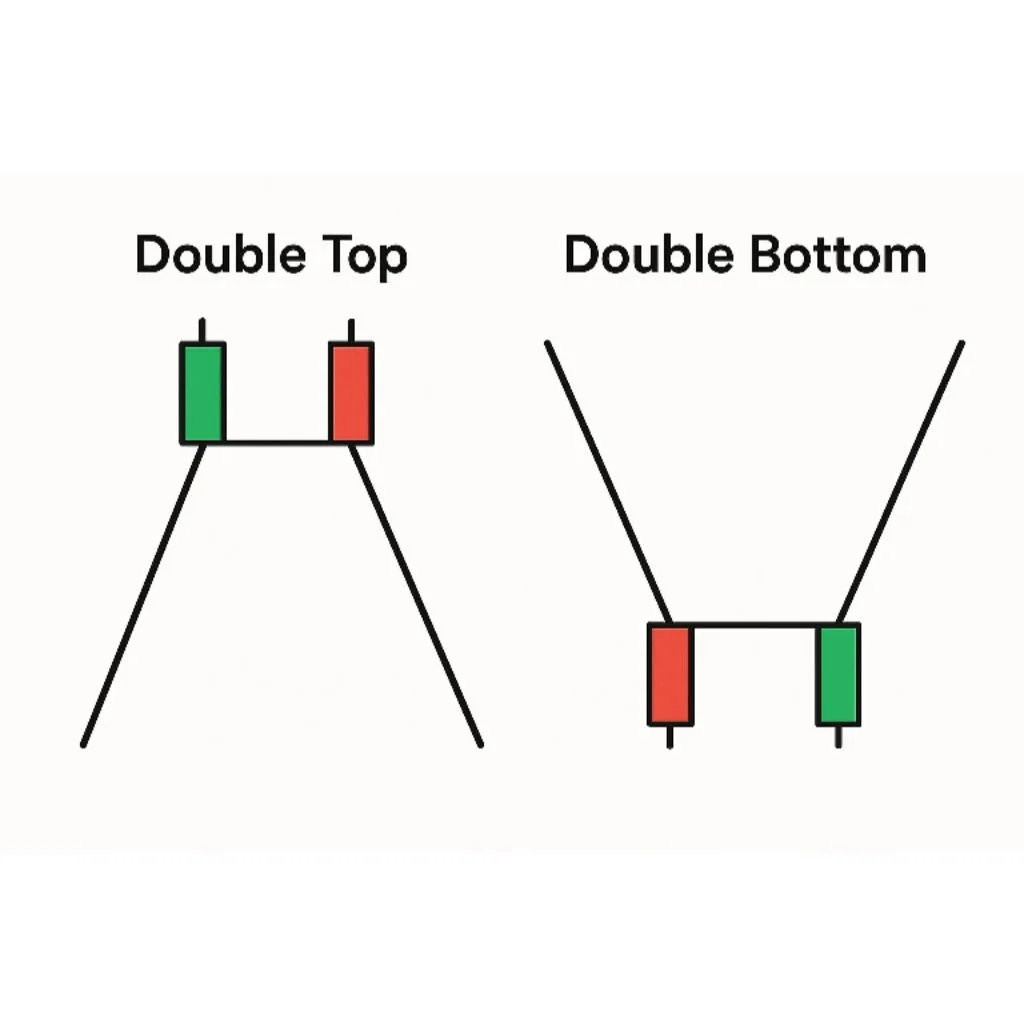
Reversal signals
Double top = bearish, Double bottom = bullish
3. Triangles (Ascending, Descending, Symmetrical)
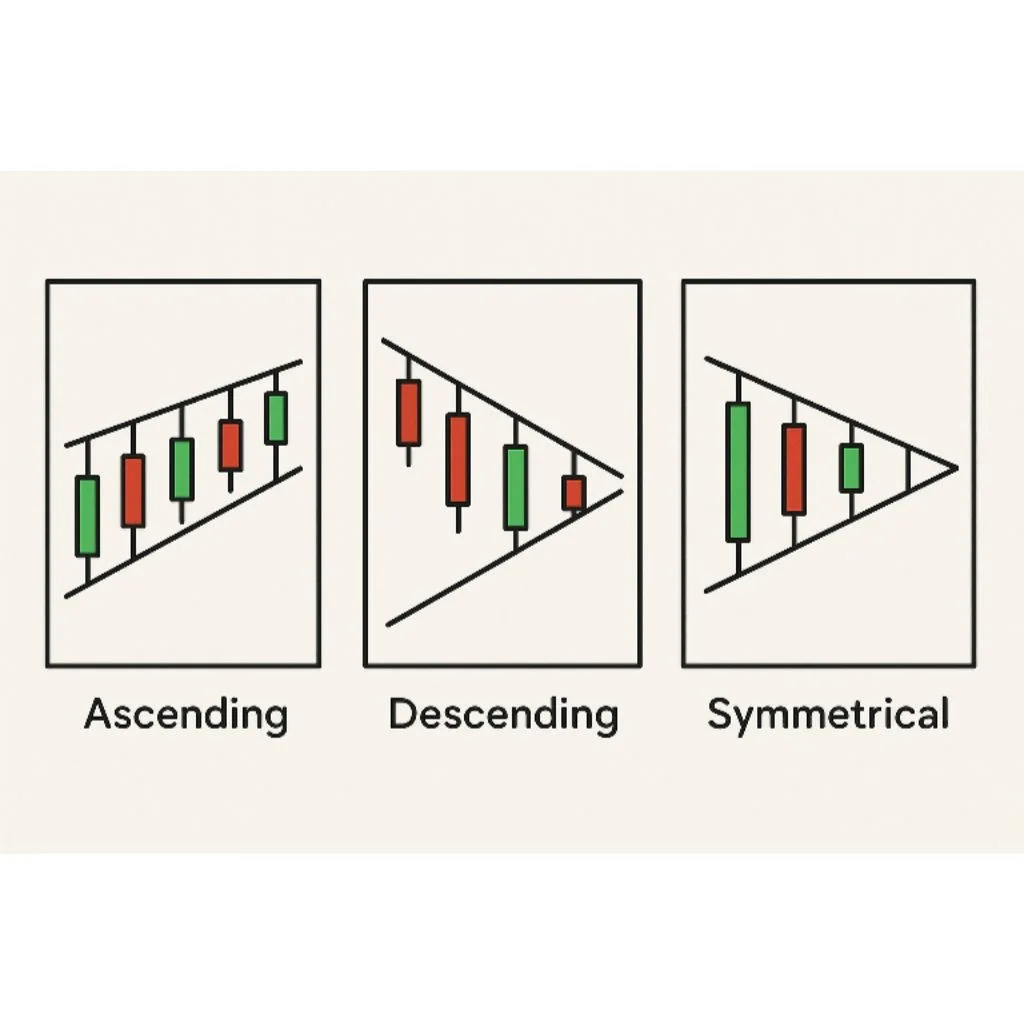
Continuation patterns
Show consolidation before breakout
4. Flags and Pennants
Short-term continuation patterns
Often follow strong price moves
Timeframes in Technical Analysis
Different traders use different timeframes based on their goals:
Trader Type Time frame Used
Scalper 1-minute to 5-minute
Day Trader 5-minute to 15-minute
Swing Trader 1-hour to daily
Position Trader Daily to weekly
Timeframes also affect signal reliability. Higher timeframes usually give stronger, more reliable signals.
Limitations of Technical Analysis
While powerful, technical analysis has some limitations:
Lagging Indicators: Most indicators are based on past data and may react late.
False Signals: Patterns may not always work as expected.
Subjective Interpretation: Different traders may read the same chart differently.
Ignores Fundamentals: Technical analysis doesn’t consider earnings, news, or economic events.
Pro Tip: Combine technical analysis with fundamental analysis for better accuracy.
Final Thoughts
Technical analysis is a powerful tool that helps traders make informed decisions using charts, indicators, and patterns. Whether you’re trading stocks, crypto, or forex, understanding technical analysis can give you a competitive edge.
However, no method guarantees success. Always combine your analysis with proper risk management, backtesting, and real-world experience.
Note: This is just an introductory guide. More in-depth analysis, advanced strategies, and real-world examples are coming soon. Stay connected to keep learning and mastering technical analysis!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is technical analysis good for beginners?
Yes, with proper learning and practice, beginners can effectively use technical analysis. Start with basic charts and indicators before moving to advanced strategies.
Q2. Can technical analysis predict the future?
It can’t predict the future with 100% accuracy, but it helps identify probabilities and potential outcomes based on historical patterns.
Q3. What is the best technical indicator?
There’s no single “best” indicator. Most traders use a combination like RSI, Moving Averages, and MACD for balanced insights.

BBW News Desk is the editorial team of BigBreakingWire, a digital newsroom focused on global finance, markets, geopolitics, trade policy, and macroeconomic developments.
Our editors monitor government decisions, central bank actions, international trade movements, corporate activity, and economic indicators to deliver fast, fact-based reporting for investors, professionals, and informed readers.
The BBW News Desk operates under the editorial standards of BigBreakingWire, prioritizing accuracy, verified information, and timely updates on major global developments.









Be First to Comment