India’s economy is set for strong growth in 2024, with Moody’s projecting a 7.2% expansion, driven by robust household consumption and moderating inflation. The country’s favorable conditions, supported by strategic policies, place it as a standout performer globally.
Key Growth Drivers
Household Consumption: Increased rural spending, aided by a strong monsoon, and high demand during the festive season are expected to support economic activity.
Inflation Trends: Despite continued food price volatility, inflation is expected to ease, coming closer to the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) target range.
Monetary Policy Outlook
Tight Monetary Policy: The RBI is expected to maintain a cautious stance on interest rates, keeping them relatively tight to manage inflation, especially in light of geopolitical and climate risks.
Global Economic Context
G-20 Growth: Growth across G-20 economies is forecast to slow to 2.8% in 2024, down from 3.0% in 2023, with moderation continuing through 2026.
Regional Performance:
US: The US economy is expected to outperform other developed nations, but growth will slow.
China: Growth will decelerate despite stimulus efforts, reflecting deeper structural challenges.
Europe: Economic recovery in Europe is expected to be slow but gradual.
India’s Long-Term Outlook
India’s GDP is expected to continue growing at a healthy pace, with Moody’s forecasting 6.6% growth in 2025 and 6.5% in 2026. Strong domestic fundamentals, including favorable policy measures and a focus on infrastructure, will support long-term growth.
Moody’s highlighted that India’s economy is currently in a “sweet spot,” balancing solid growth and moderating inflation. The economy grew by 6.7% in the second quarter of 2024, driven by household consumption, investment, and manufacturing activity. High-frequency indicators like strong manufacturing, services, and consumer optimism signal continued momentum.
Inflation Risks and Challenges
While inflation in India has spiked recently due to a surge in vegetable prices, it is expected to moderate as food prices stabilize. Moody’s anticipates that inflation will return to the RBI’s target range as sowing increases and food stocks remain adequate. However, risks remain from geopolitical tensions and extreme weather events.
The RBI’s monetary policy stance remains cautious, despite shifting to a neutral position and holding the repo rate steady at 6.5% in October. The central bank is likely to keep policies tight in 2024, given the solid growth outlook and inflation risks.
Supportive Factors for Growth
India’s strong economic fundamentals, including healthy corporate and bank balance sheets, a strong external position, and ample foreign exchange reserves, provide a solid foundation for continued growth. Rising capacity utilization, improving business sentiment, and government infrastructure spending are also expected to boost private investment.
Overall, Moody’s outlook for India’s economy remains positive, with expectations for steady growth through 2026 despite global uncertainties.
Meanwhile, CLSA has reversed its October strategy, reallocating funds back to India with a 20% overweight position. This shift is due to China’s economic challenges and market corrections under Trump’s potential re-election. Both MSCI China and India saw a ~10% correction, resulting in no significant losses.
India’s inflation reached a 14-month peak of 6.21% in October, surpassing predictions and the central bank’s target, potentially delaying rate cuts. Inflation in September was 5.49%. The 10-year bond yield increased to 6.83%, rising by one basis point after a prior gain of three points.
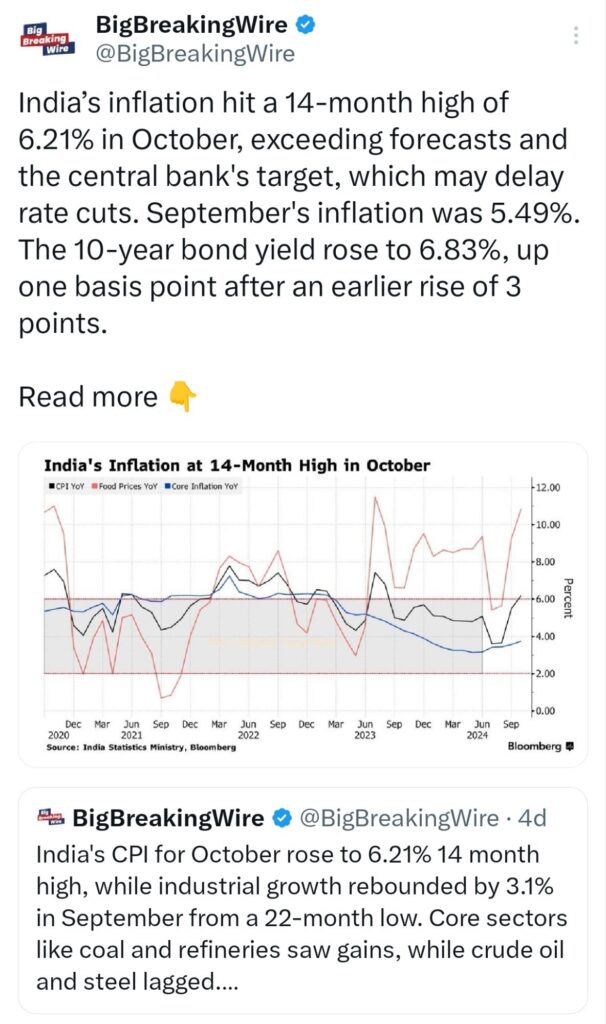
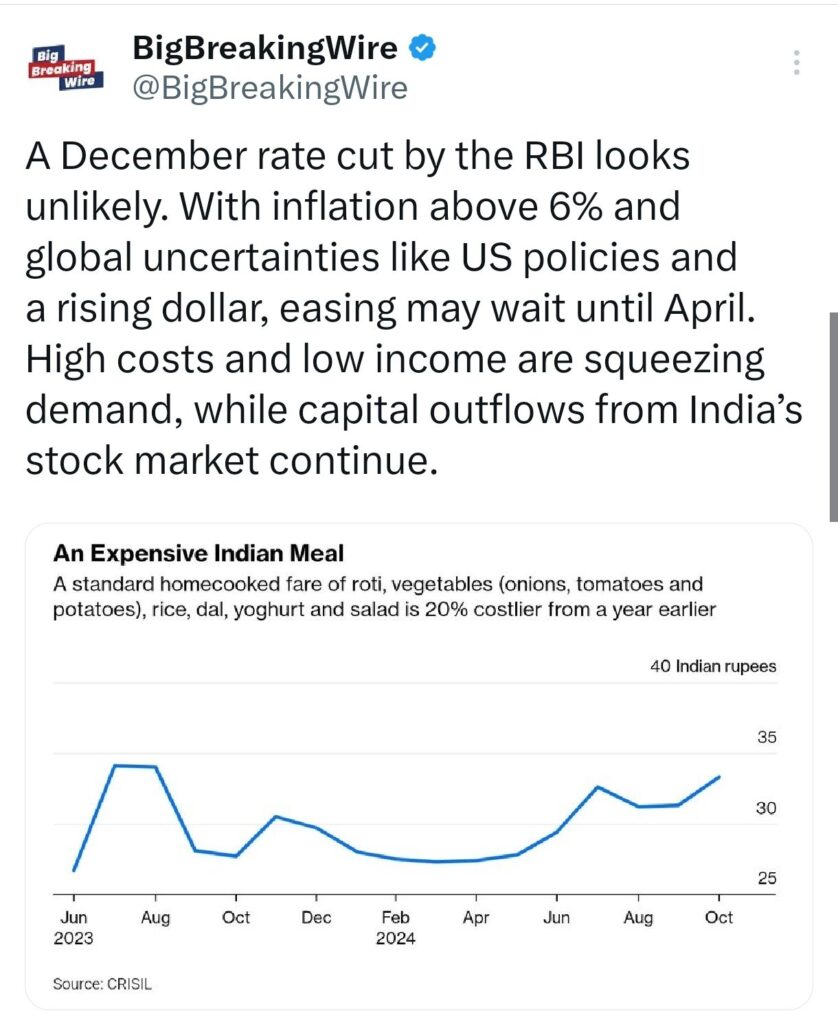
A rate cut by the RBI in December seems unlikely due to inflation exceeding 6% and global uncertainties, such as US policies and a strengthening dollar. Easing may be delayed until April. Rising costs and low income are pressuring demand, while capital outflows from India’s stock market persist.
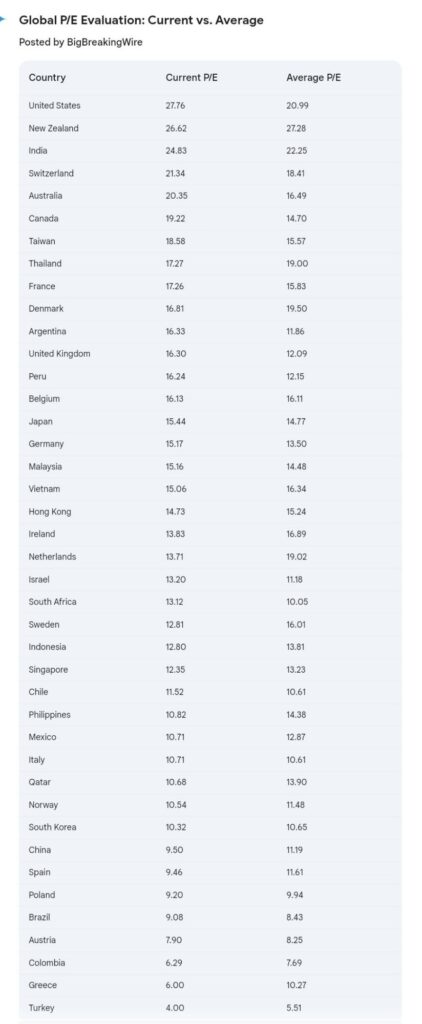
India has fallen to 3rd place in the global P/E ratio rankings, with the U.S. now leading. India had held the top spot as of October 7.
Goldman Sachs Forecasts 6.3% GDP Growth for India in 2025, Below Consensus
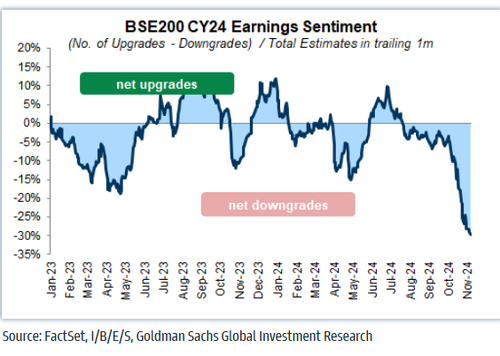
According to a Goldman Sachs trader, it’s clear that urban consumption is slowing down, affecting major brands like Nestle, Unilever, KFC, and Asian Paints. The Indian market doesn’t have the support for investors to just wait and see if this slowdown is temporary or will last longer. The slowdown is happening at a time when the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is focusing on reducing unsecured loans, which doesn’t seem like a coincidence. Inflation is also a challenge for consumption, with October’s inflation rate coming in higher than expected at 6.2%, up from 5.5% in September.
Despite weaker earnings and growing concerns about the economy, investments in equity mutual funds rose 20% month-over-month, reaching a record $5 billion in October. Right now, the market is torn between strong fundamentals and these challenges.
Goldman Sachs’ economists expect India’s GDP growth to be lower than expected in 2025, at 6.3% (40 basis points below consensus). India is focusing on fiscal consolidation and slowing credit growth, partly due to the RBI’s actions. For the US, Goldman Sachs is more optimistic than others, predicting 2.5% growth in 2025. They believe the second Trump administration will bring higher tariffs on China, fewer immigrants, tax cuts, and regulatory changes, which could boost the economy. US core inflation should slow to 2.4% by the end of 2025. If tariffs rise to 10%, inflation could rise to 3%. The Federal Reserve is expected to cut rates significantly over the next year, likely bringing them down to 3.25-3.5%, with more cuts in early 2025.
HSBC Cuts 2025 BSE Sensex Target to 90,520, Citing 15% Upside and Slower Earnings Growth
HSBC Global Research has lowered its 2025 target for India’s benchmark BSE Sensex to 90,520 from 1,00,080, citing risks of earnings downgrades and high valuations. This suggests a 15% potential upside from the current level. The slowdown in earnings growth is expected to lead to a more sustainable pace, but may cause investors to reassess their positions. Despite this, India remains one of the fastest-growing markets for 2025.
The Sensex has fallen 8.46% from its peak, with mid- and small-cap indices seeing larger declines. Banks are struggling with interest margins, and the IT sector faces weak demand. Economic growth in India is expected to slow from 8.2% in 2023 to 6.5% in 2025. Consumption demand is weakening, and key economic indicators have underperformed. HSBC also notes that small and mid-cap stocks are expected to grow faster than large-cap stocks. Meanwhile, HSBC sees a 21% upside for China’s equities but warns of challenges for Japan due to a stronger yen.
Retail loan defaults in India are rising due to aggressive lending practices, leading to increased stress in the stock market. Major lenders like Kotak Mahindra Bank and IndusInd Bank are seeing difficulties with unsecured loans, while smaller lenders are experiencing even bigger declines. This situation is raising concerns about future economic risks, and analysts predict that things could remain tough if consumer demand does not pick up.
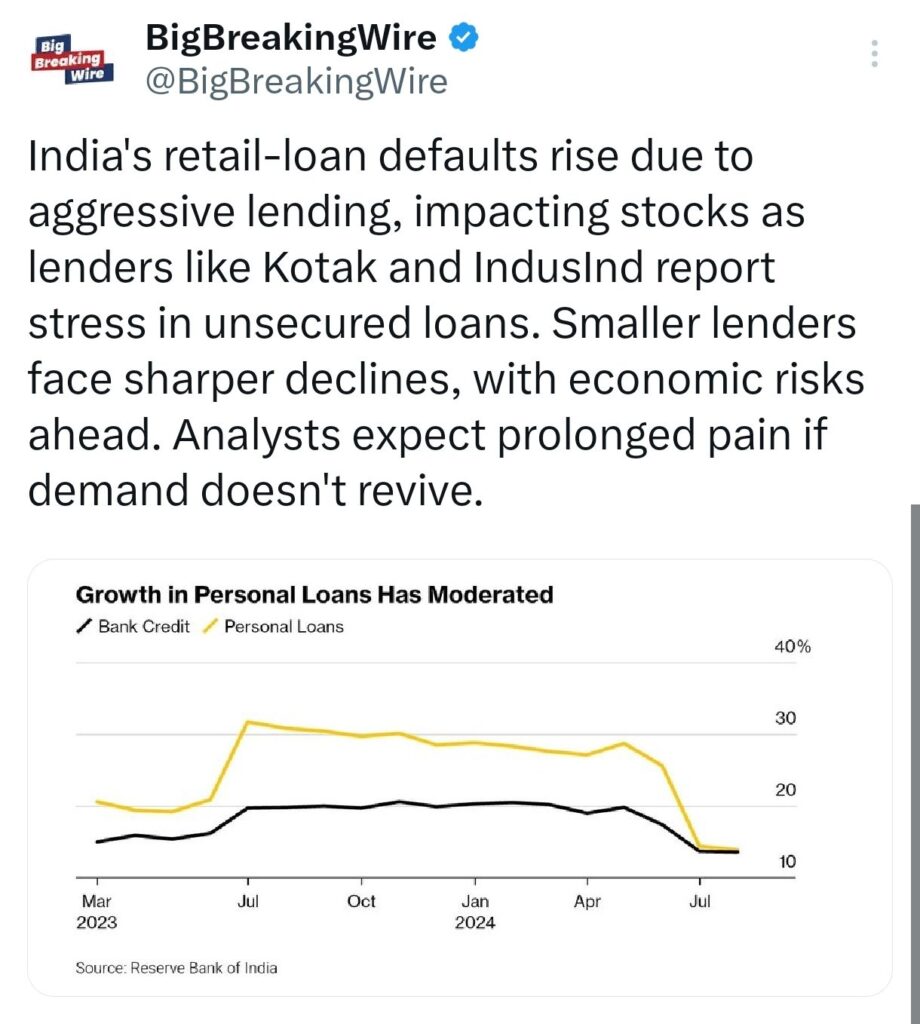
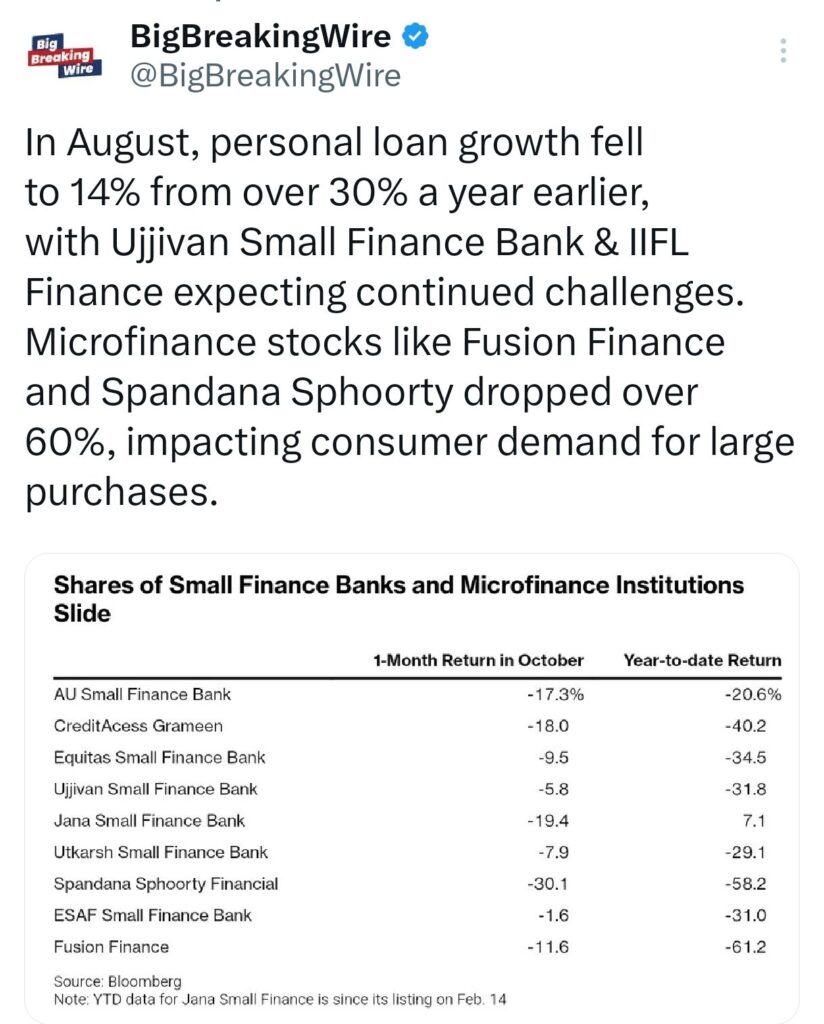
In August, the growth rate of personal loans dropped significantly to 14% from over 30% the previous year. Banks like Ujjivan Small Finance Bank and IIFL Finance are anticipating more challenges ahead. Microfinance companies such as Fusion Finance and Spandana Sphoorty have seen their stock prices fall by more than 60%, which is also affecting consumer spending on big-ticket items.
Bringing you the latest updates on finance, economies, stocks, bonds, and more. Stay informed with timely insights.




































Be First to Comment