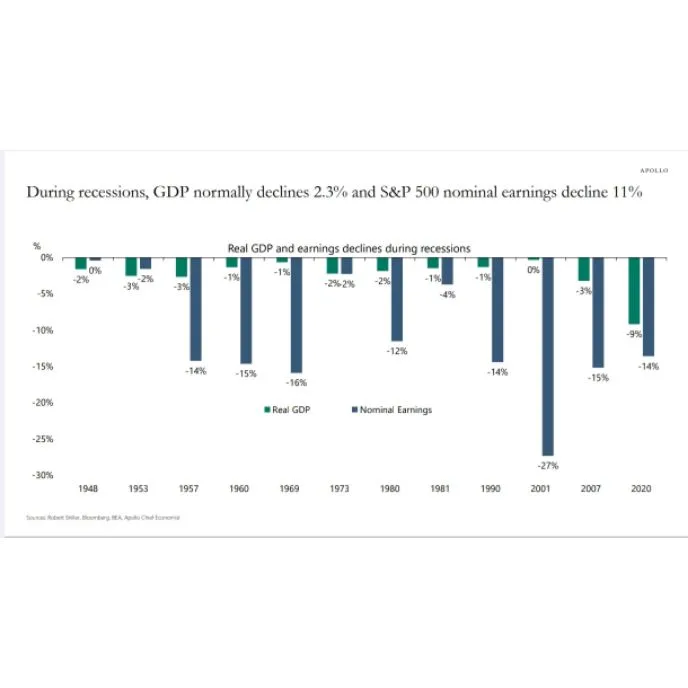
According to an analysis by Apollo Chief Economist using data from Robert Shiller, Bloomberg, and the BEA, recessions have consistently led to declines in both real GDP and corporate earnings.
Key Highlights:
On average, U.S. real GDP drops by 2.3% during recessions.
Meanwhile, S&P 500 nominal earnings fall by around 11%.
The most severe EPS (Earnings Per Share) decline was during the 2001 recession, with a sharp 27% drop in earnings.
The worst GDP decline occurred in 2020, reflecting the economic shock from the COVID-19 pandemic, where GDP contracted by 9% and earnings fell by 14%.
Other significant declines include:
2007–08 crisis: GDP fell 3%, earnings dropped 15%
1980 recession: GDP down 2%, earnings down 12%
1957 recession: GDP down 3%, earnings down 14%
Conclusion: This historical pattern shows that economic downturns lead to moderate contractions in GDP but often result in much steeper declines in corporate profits. Investors and policymakers should be prepared for double-digit earnings hits even if GDP losses appear modest.

One Comment